Cybersecurity Monthly Report (January 2025)
Cybersecurity Monthly Report (January 2025)
< Overall Threat Trend >
Ex ante joint defense and monitoring
A total of 79,566 pieces of government agency cybersecurity joint defense intelligence were collected this month (a decrease of 3,539 from the previous month). Analyzing the types of identifiable threats, the top one was information collection (40%), i.e., mainly obtaining information through attacks such as scanning, detection, and social engineering; followed by malicious content (24%), mostly spreading inappropriate content in the forms of text, photos, videos, etc.; and intrusion attempts (16%), most dominated by attempts to intrude into unauthorized hosts. The distribution of intelligence volume in the past year is as shown in Figure 1.
After further compilation and analysis of joint defense information, it was discovered that recent hackers have impersonated the National Institute of Cyber Security to launch targeted social engineering email attacks Taiwanese academic institutions. In the name of “Cyber Security Attack Warning”, the emails urge recipients to run ransomware detection tools in response to ransomware attack activities. However, the actual intent is to deceive recipients into downloading and executing malicious attachments. Relevant intelligence has provided government agencies with recommendations on joint defense and monitoring.
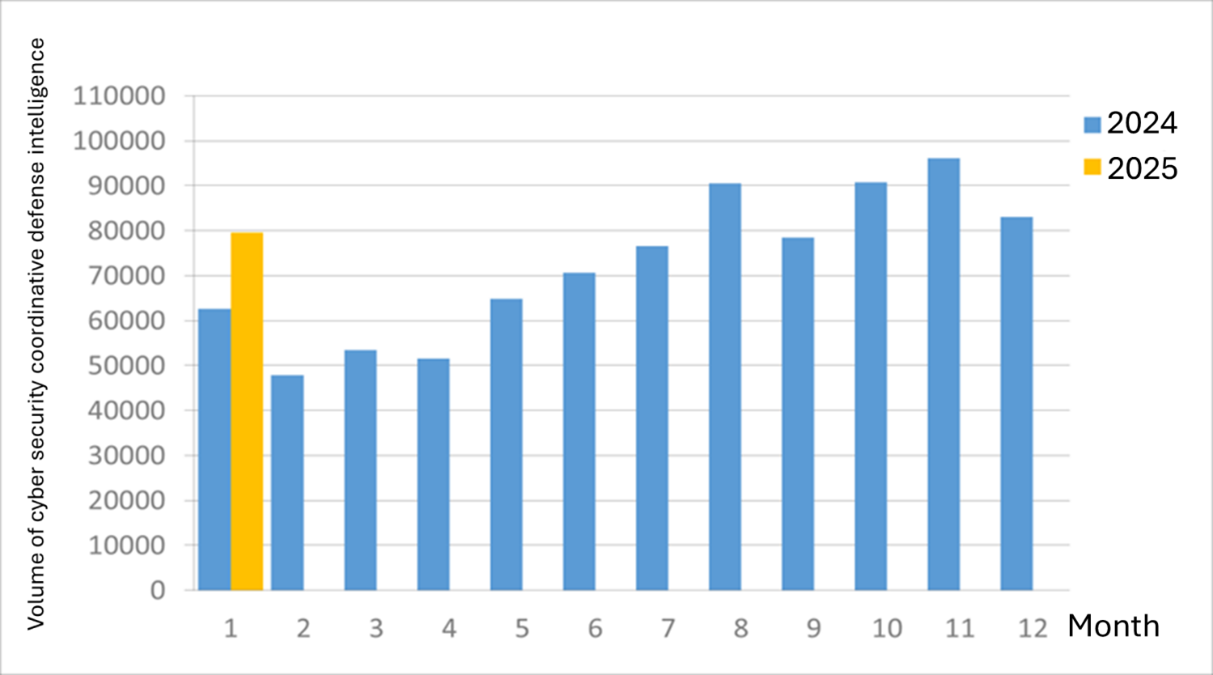
Figure 1 Statistics of cybersecurity monitoring intelligence in joint defense
In-process reporting and responding
The number of cyber security incident reports totaled 47 this month (an increase of 7 from the previous month), which is 0.61 times the number from the same period last year. This month, some agencies were under the attack of blocking services, resulting in a slowdown or interruption of website services, which accounted for 12.77% of the total number of reports. The statistics of cyber security incident reports in the past year are as shown in Figure 2.
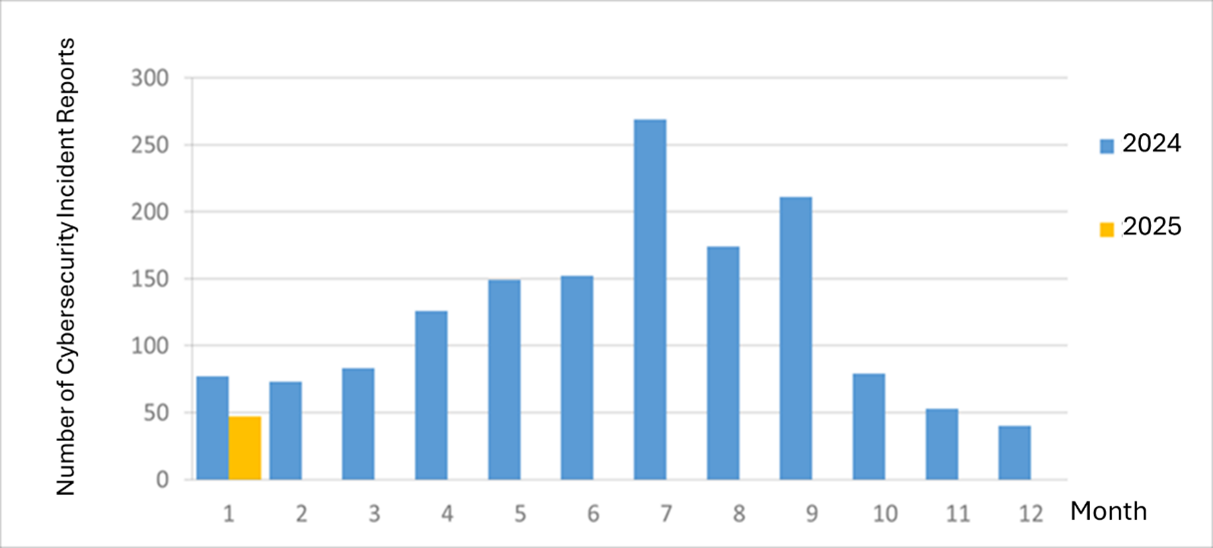
Figure 2 Number of cybersecurity incident reports
Post information sharing
This month, during an event organized by a certain agency, the event brochure was placed in Google Cloud for the public to download. However, the contracted vendor also uploaded registration information containing personal data to the same cloud space. The access permissions were not properly configured, allowing unauthorized users to access the relevant data, resulting in a personal data leakage incident. After the incident, the agency immediately removed the registrant data from the cloud space and notified the affected individuals in accordance with the relevant provisions of the "Personal Data Protection Act" to reduce potential impact and risk.
【Additional Reference】
When government agencies organize short-term activities, they use cloud space for document sharing and registration data management to improve operational efficiency and convenience. However, if access permissions are not properly controlled, it may lead to the leakage of sensitive data. It is recommended that agencies refer to the relevant provisions in the "Personal Data Protection Act" and the "Cybersecurity Reference Guidelines for Cloud Services Used by Government Agencies" to ensure that when using cloud space to store data, public documents and files containing personal data are stored in different cloud directories or separate storage spaces. Additionally, appropriate access permissions should be set up to protect against unauthorized third-party access or downloads.
In addition, when entrusting activities to vendors, personal data protection responsibilities should be clearly stated in the contract, including data storage methods, access restrictions, retention periods, and deletion mechanisms etc. Personal data should be removed or archived immediately after the event, and personal data should not be stored in cloud storage to reduce the risk of personal data leakage.